

The sequence of these bases determines the genetic information encoded in DNA. The four nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. It does not store any personal data.DNA structure and biochemical composition: DNA is a double-stranded helix made up of nucleotides. The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin.
The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other.
The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly.

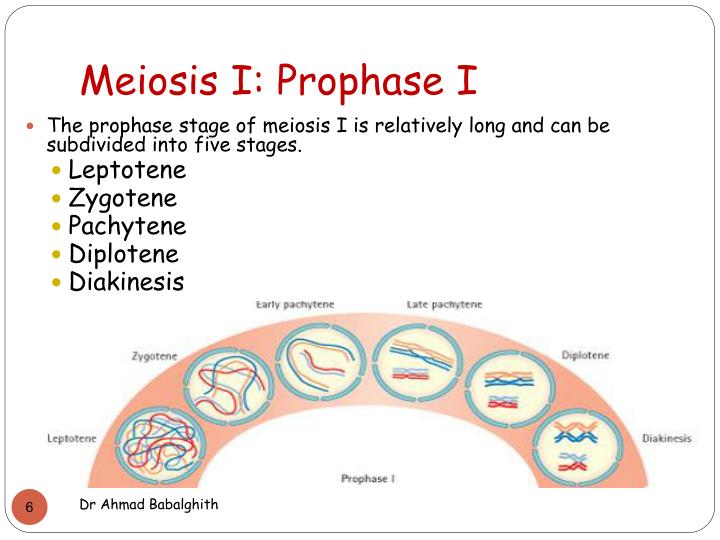
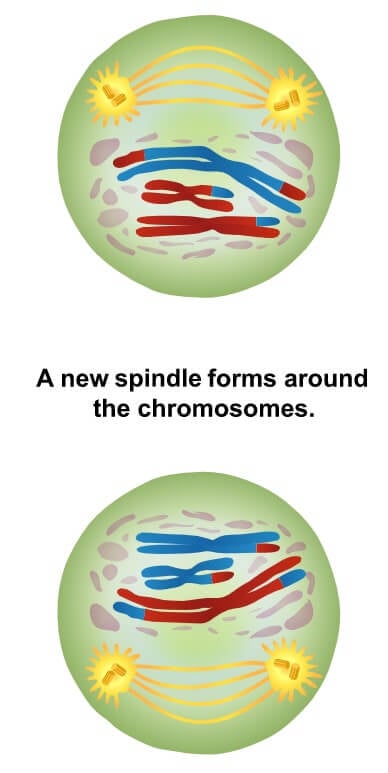
Spindle fibres attach to the chromosomes at points along the chromosomes called centromeres. This process is known as crossing over, and the points at which this occurs on a chromosome are referred to as chiasmata. To further increase genetic diversity, homologous chromosomes exchange small parts of themselves, such that one chromosome contains both maternal and paternal DNA. Spindle fibres appear which are important for the successful division of the chromosomes. The nuclear envelope disintegrates and the chromosomes begin to condense. There are initially four chromatids (c) and two chromosomes (n) for each of the 23 chromosome pairs (4c, 2n). Prior to prophase, chromosomes replicate to form sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are separated into two cells such that there is one chromosome (consisting of two chromatids) per chromosome pair in each daughter cell, i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
